Managing risk
Managing risk for shipping and logistics
Risk management is Identifying and Management!
Managing risk of AIM is the identification, inspection of risks to monitor and control the occurrence or effects to assurance and safety in shipping and logistics.
Managing risks in shipping
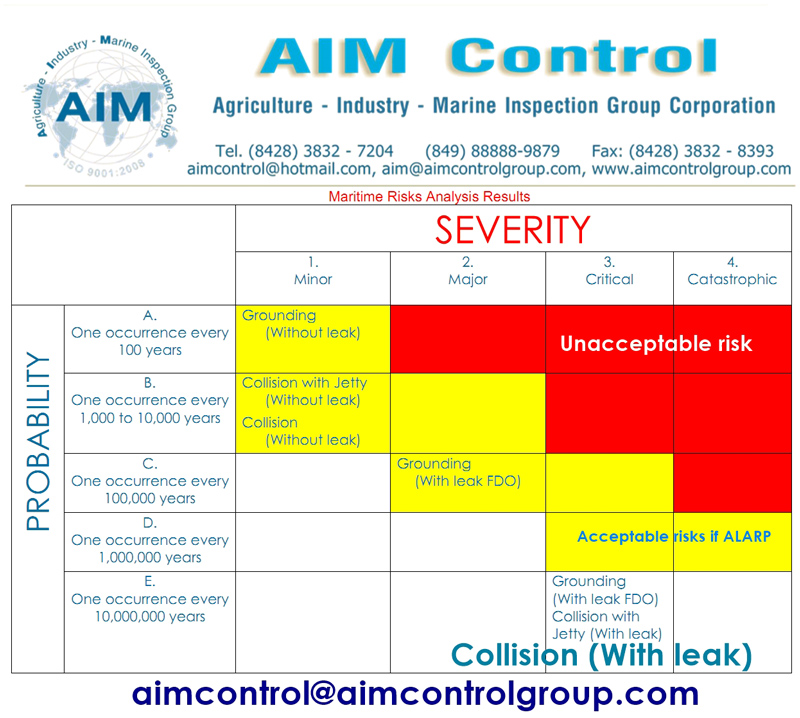
According to International Maritime Organization (IMO), risk is the “combination of the frequency and the severity of the consequence”, the probability of severity of the (un)predictable consequences.
the ISM Code (International Safety Management Code)
Identifying
In shipping, Risks are exposed the extremely levels for Ships at sea encounter the natural perils of fog, bad weather, typhoons, blizzards and rain and the precipitous storm wave.
Managing
In this environment the cargo has to be carefully carried and delivered to destinations.
called hazards and risks in the adventure.
The hull and machinery underwriters and protection and indemnity clubs enables the owner to ensure against the perils of the sea and so avoid a level of risks which if left uninsured may bankrupt the company.
To insurers by shipowners or their managers requires expert in managers of risk in shipping to analysing problems, identifying hazards and putting in place structures which enable the development of more effective working practices and also provides a way of improving communication which recognises the management of risk as an inter-linking discipline.
Risk Managing in shipping is used for
-
individuals,
-
organisations,
-
companies and
-
government departments
to link between commercial and technical risks are discussed.
-
The seafaring and port risks are safety,
-
The authority and maritime.
The Marine Risk Assessment Process
-
Identification of hazards
-
Assessment of the risks concerned
-
Application of controls to reduce the risks
-
Monitoring of the effectiveness of the controls
Also it is important to keep in mind that “hazards” must not be confused with “incidents” whereas incidents must not denote consequences.
The most relevant risks to monitor are:
-
Health and safety issues of individuals involved directly or indirectly in the activity, or those who may be otherwise affected
-
Property of the company and others
-
The environment
Main of Risk management
-
Risk management in shipping
-
Risk managed in shipping companies
-
Supply chain risk management
-
Managing risk in trading and transporting cargoes
-
Managing safety and Control risk on board ship
-
Managing and safety in ports
-
Managing through marine insurance on risks
-
Managing project through of risks design and newbuilding
-
Managing through risks of legislation
Risk management has evolved a lot through time, and in many different directions
-
Political risks
-
Substitution of oil
-
Technological changes
-
Macroeconomic development
-
Freight rate fluctuation
-
Bunker fluctuation
-
Sales and purchasing
-
Compliance with relevant maritime regimes
-
Vessel utilization
-
Safety operation of ship
-
Terrorism and piracy
-
Experienced seafarers and staff
-
Compliance with environment regulation
-
Fraud
-
Insurance coverage
-
Funding and liquidity
-
Interest rate risks
-
Currency risk
-
Counterpart risks
-
Perils;
-
Poor handling;
-
Inadequate packing;
-
Inadequate stowage;
-
Heavy weather;
-
Pilferage and
-
Non-delivery
-
Threats to Cargo
-
Theft at warehouses and distribution centers
-
Theft from trailers
-
Theft from loading/ unloading
-
Risks of operation
-
Hijacking/piracy
-
Loss and damage to cargo
-
Delays or disruption of supply chain
-
Unexpected additional costs
-
Personal injury or death
-
Increased insurance premiums
-
Increased prices of goods for consumers
-
Loss of insurance coverage
-
Payment disputes or no payment
-
Others

Awareness and control.
Implement effective preventative strategies.
Deliver and receipt tangible improvements / measurable results.
The supply chain.
Utilise knowledge and experience
Take ownership and control of the risk management process.